Tropics Tracker
Atlantic Basin • Caribbean Sea • Gulf of America
Current Tropical Activity
Tropical Weather Outlook



Current Weather Along U.S. Coast
Gulf Coast
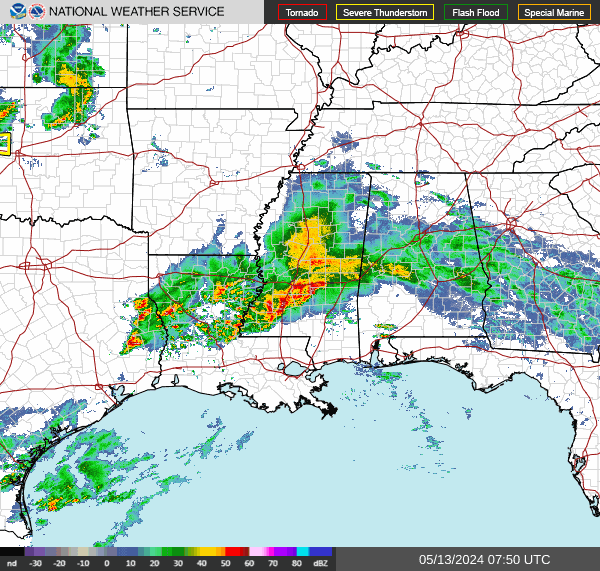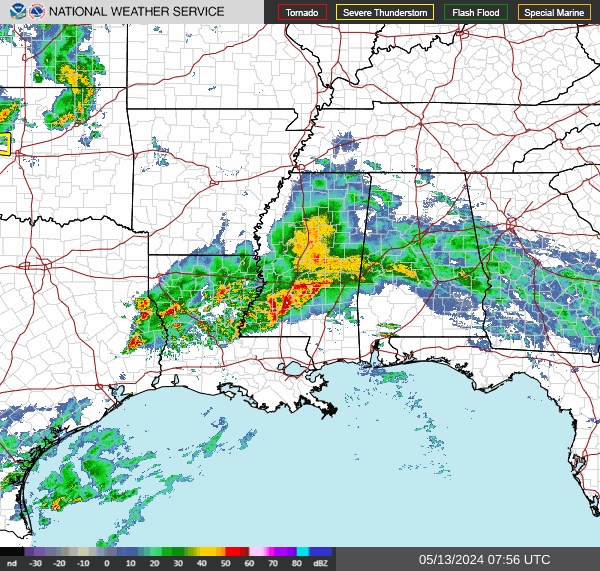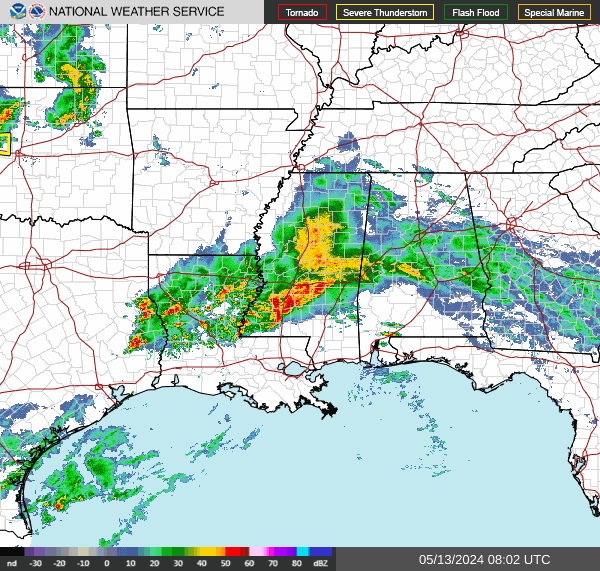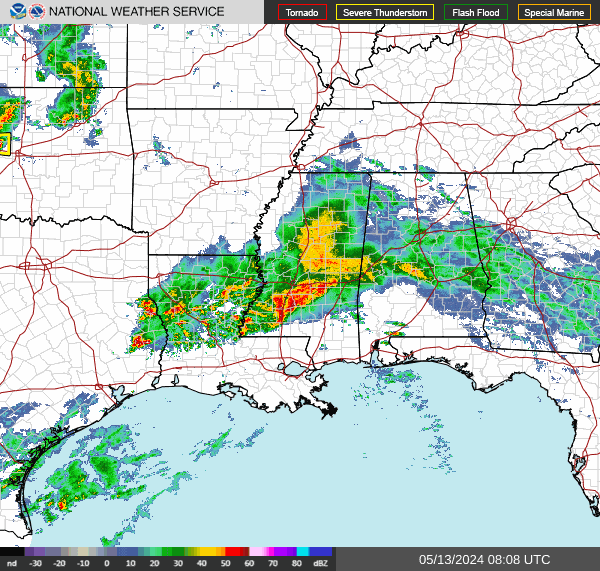
Southeast
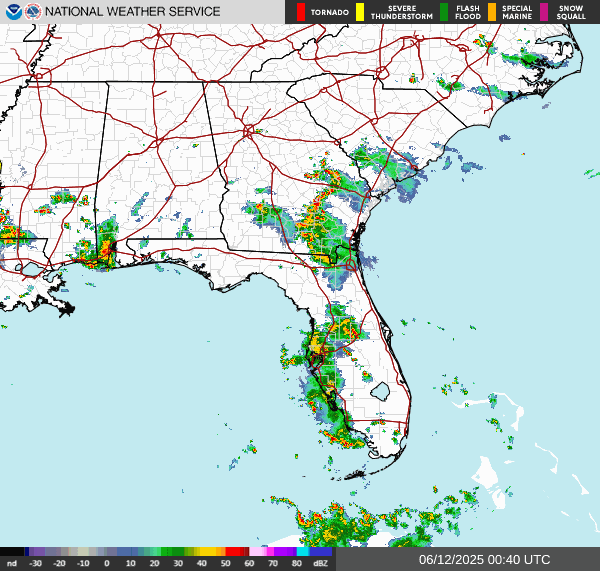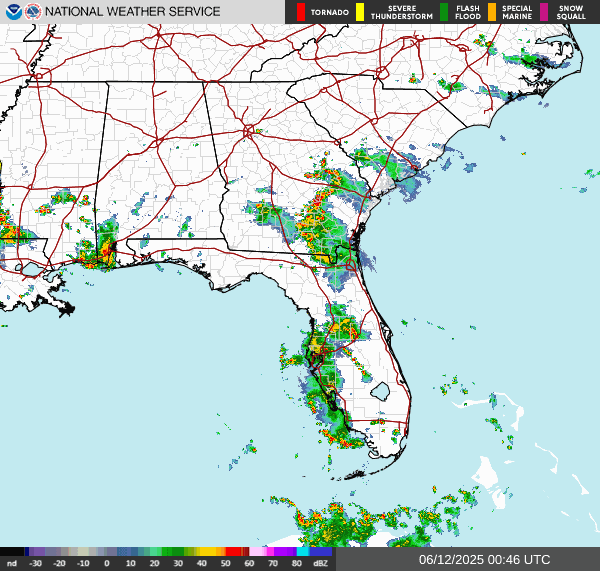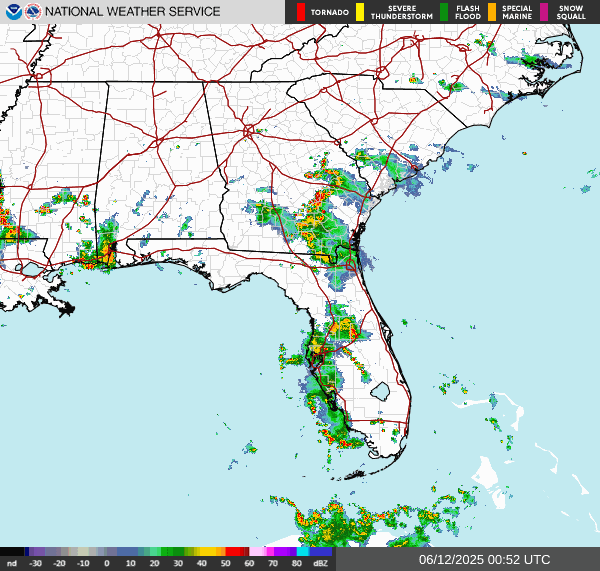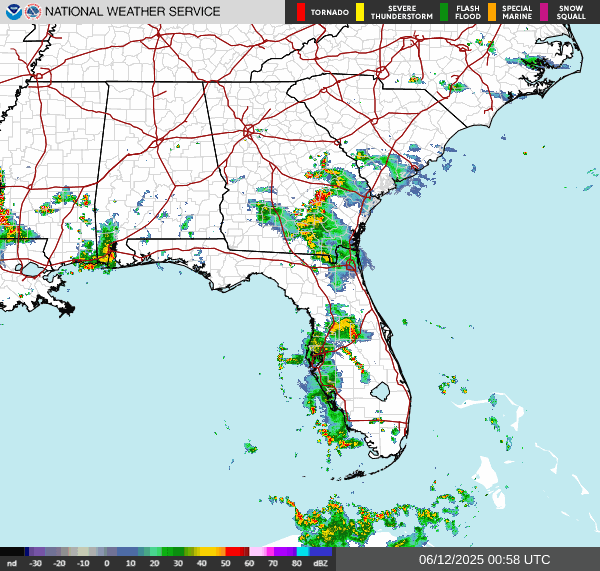
Northeast
Potential Tropical Cyclone: Disturbances with a high chance at becoming tropical, and pose the threat of tropical storm-force winds to landmasses within 48 hours.
Tropical Depression: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 38 mph or less.
Tropical Storm: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 39 to 73 mph.
Hurricane: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 74 mph or higher.
Post-Tropical Cyclone: A post-tropical cyclone is formed when the typical characteristics of a tropical cyclone are replaced with those of extratropical cyclones.
Hurricane Warning: An announcement that sustained winds of 64 knots (74 mph or 119 km/hr) or higher are expected somewhere within the specified area in association with a tropical, subtropical, or post-tropical cyclone. Because hurricane preparedness activities become difficult once winds reach tropical storm force, the warning is issued 36 hours in advance of the anticipated onset of tropical-storm-force winds. The warning can remain in effect when dangerously high water or a combination of dangerously high water and waves continue, even though winds may be less than hurricane force.
Hurricane Watch: An announcement that sustained winds of 64 knots (74 mph or 119 km/hr) or higher are possible within the specified area in association with a tropical, subtropical, or post-tropical cyclone. Because hurricane preparedness activities become difficult once winds reach tropical storm force, the hurricane watch is issued 48 hours in advance of the anticipated onset of tropical storm force winds.
Storm Surge Warning: The danger of life-threatening inundation from rising water moving inland from the shoreline somewhere within the specified area, generally within 36 hours, in association with an ongoing or potential tropical cyclones, a subtropical cyclone or a post-tropical cyclone. The warning may be issued earlier when other conditions, such as the onset of tropical-storm-force winds are expected to limit the time available to take protective actions for surge (e.g., evacuations). The warning may also be issued for locations not expected to receive life-threatening inundation but which could potentially be isolated by inundation in adjacent areas.
Storm Surge Watch: The possibility of life-threatening inundation from rising water moving inland from the shoreline somewhere within the specified area, generally within 48 hours, in association with an ongoing or potential tropical cyclones, a subtropical cyclone or a post-tropical cyclone. The watch may be issued earlier when other conditions, such as the onset of tropical-storm-force winds are expected to limit the time available to take protective actions for surge (e.g., evacuations). The warning may also be issued for locations not expected to receive life-threatening inundation but which could potentially be isolated by inundation in adjacent areas.
Tropical Storm Warning: An announcement that sustained winds of 34 to 63 knots (39 to 73 mph or 63 to 118 km/hr) are expected somewhere within the specified area within 36 hours in association with a tropical, subtropical, or post-tropical cyclone.
Tropical Storm Watch: An announcement that sustained winds of 34 to 63 knots (39 to 73 mph or 63 to 118 km/hr) are possible within the specified area within 48 hours in association with a tropical, subtropical, or post-tropical cyclone.
Along the coast, storm surge is often the greatest threat to life and property from a hurricane. In the past, large death tolls have resulted from the rise of the ocean associated with many of the major hurricanes that have made landfall. Hurricane Katrina (2005) is a prime example of the damage and devastation that can be caused by surge. At least 1,500 persons lost their lives during Katrina and many of those deaths occurred directly, or indirectly, as a result of storm surge.
Storm surge is an abnormal rise of water generated by a storm, over and above the predicted astronomical tides. Storm surge should not be confused with storm tide, which is defined as the water level rise due to the combination of storm surge and the astronomical tide. This rise in water level can cause extreme flooding in coastal areas particularly when storm surge coincides with normal high tide, resulting in storm tides reaching up to 20 feet or more in some cases.
Additional storm surge information can be found on the National Hurricane Center's Storm Surge Overview .
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a 1 to 5 rating based on a hurricane's sustained wind speed. This scale estimates potential property damage. Hurricanes reaching Category 3 and higher are considered major hurricanes because of their potential for significant loss of life and damage. Category 1 and 2 storms are still dangerous, however, and require preventative measures.
Category 1 (74-95 mph): Well-constructed frame homes could have damage to roof, shingles, vinyl siding and gutters. Large branches of trees will snap and shallowly rooted trees may be toppled. Extensive damage to power lines and poles likely will result in power outages that could last a few to several days.
Category 2 (96-110 mph): Well-constructed frame homes could sustain major roof and siding damage. Many shallowly rooted trees will be snapped or uprooted and block numerous roads. Near-total power loss is expected with outages that could last from several days to weeks.
Category 3 (111-129 mph): Well-built framed homes may incur major damage or removal of roof decking and gable ends. Many trees will be snapped or uprooted, blocking numerous roads. Electricity and water will be unavailable for several days to weeks after the storm passes.
Category 4 (130-156 mph): Well-built framed homes can sustain severe damage with loss of most of the roof structure and/or some exterior walls. Most trees will be snapped or uprooted and power poles downed. Fallen trees and power poles will isolate residential areas. Power outages will last weeks to possibly months. Most of the area will be uninhabitable for weeks or months.
Category 5 (157 mph or higher): A high percentage of framed homes will be destroyed, with total roof failure and wall collapse. Fallen trees and power poles will isolate residential areas. Power outages will last for weeks to possibly months. Most of the area will be uninhabitable for weeks or months.
Source National Hurricane Center